ipvsadm: Linux的负载均衡功能ipvs的使用,ipvsadm的常用操作命令
目录
说明
ipvs是内置在linux kernel中的传输层负载均衡器,IP Virtual Server。
支持两种协议: tcp、udp,三种模式:NAT、tunneling、direct routing
十种均衡算法:
round robin
weighted round robin
least-connection
weighted least-connection
locality-based least-connection
locality-based least-connection with replication
destination-hashing
source-hashing
shortest expected delay
never queue
管理程序ipvsadm
ipvs的管理程序是ipvsadm:
yum install -y ipvsadm
ipvs的手册很详细:
$ man ipvsadm
ipvsadm -A|E -t|u|f service-address [-s scheduler]
[-p [timeout]] [-M netmask] [-b sched-flags]
ipvsadm -D -t|u|f service-address
ipvsadm -C
ipvsadm -R
ipvsadm -S [-n]
ipvsadm -a|e -t|u|f service-address -r server-address
[-g|i|m] [-w weight] [-x upper] [-y lower]
ipvsadm -d -t|u|f service-address -r server-address
ipvsadm -L|l [options]
ipvsadm -Z [-t|u|f service-address]
ipvsadm --set tcp tcpfin udp
ipvsadm --start-daemon state [--mcast-interface interface]
[--syncid syncid]
ipvsadm --stop-daemon state
ipvsadm -h
-A|E:增加、编辑virtual service
-t|u|f:tcp、udp、firewall-mark
-s:调度算法rr、wrr、lc、wlc、lblc、lblcr、dh、sh、sed、nq
-p:开启会话保持,将同一个client的请求转发到同一个real server
-M:子网掩码,在会话保持中,源IP来自同一个子网的请求,被认为是同一个client
-b:设置sched-flags
-D:删除virtual service
-C: 晴空virtual server
-R:重新载入virtual server规则
-S:导出virtual server规则
-n:直接显示IP和端口
-a|e:为指定的virtual service添加、编辑real server
-r:real server地址
-g|i|m: 直接路由模式、ipip隧道模式、NAT模式
-w:real server的权重
-x:real server接收的连接上限,超过上限不在接收连接请求
-y:real server重新开始接收连接的上限,连接数低于设置数值,开始接收新连接
-d:从指定virtual service中删除virtual server
-L|l:列出virtual service和virtual server
-Z:计数清零
--set:设置tcp、tcp after fin、udp的超时时间
--start-daemon:启动连接同步进程,可设置为master和backup模式,master将会话信息同步到backup中
--stop-daemon:停止同步进程
转发模式:直接路由(-g)、ipip隧道(-i)、NAT(-m)
ipvs支持直接路由(-g)、ipip隧道(-i)、NAT(-m)三种转发模式:
-g, --gatewaying Use gatewaying (direct routing). This is the default.
-i, --ipip Use ipip encapsulation (tunneling).
-m, --masquerading Use masquerading (network access translation, or NAT).
在规则中的体现如下:
ipvsadm -a -t 192.168.40.2:80 -r 192.168.40.10:10 -g -w 1
ipvsadm -a -t 192.168.40.2:80 -r 192.168.40.11:11 -i -w 1
ipvsadm -a -t 192.168.40.2:80 -r 192.168.40.12:12 -m -w 1
各自的原理图如下:
NAT模式:Virtual Server via NAT模式中所有来往报文都经过LB,每个报文都要进行NAT。
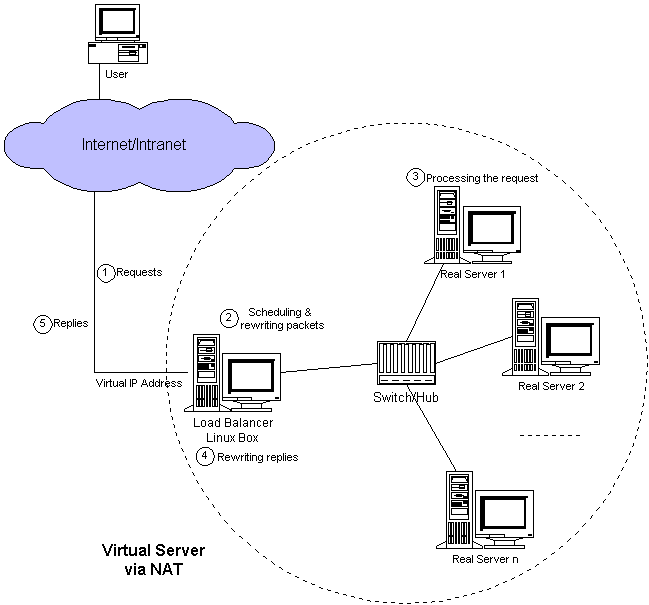
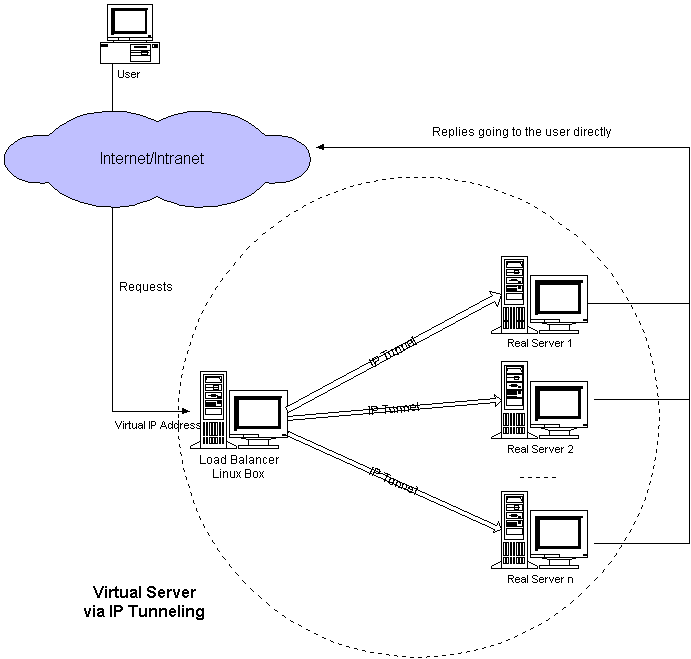
IP隧道模式:Virtual Server via IP Tunneling模式中要在lb与real server之间建立ipip隧道,real server从ipip隧道中解出原始报文,并直接回复。
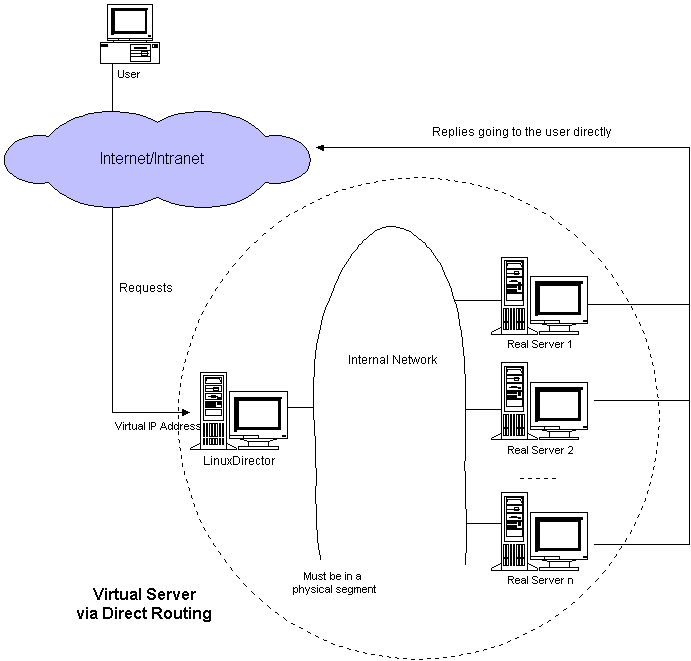
直接路由模式:Virtual Server via Direct Routing模式中LB直接将报文的目的MAC地址修改为real server的网卡地址,LB需要与real server位于同一个二层网络,并且LB和每个real server上都要设置相同的vip。
创建virtual service
添加一个服务地址192.168.40.2:80的virtual service,协议为tcp,策略为rr:
ipvsadm -A -t 192.168.40.2:80 -s rr
分别添加三个real server,各自使用不同的端口,分别使用直接路由、隧道、NAT模式:
ipvsadm -a -t 192.168.40.2:80 -r 192.168.40.10:10 -g -w 1
ipvsadm -a -t 192.168.40.2:80 -r 192.168.40.11:11 -i -w 1
ipvsadm -a -t 192.168.40.2:80 -r 192.168.40.12:12 -m -w 1
查看创建server table:
# ipvsadm-save -n
-A -t 192.168.40.2:80 -s rr
-a -t 192.168.40.2:80 -r 192.168.40.10:80 -g -w 1 <-- 注意端口被改了
-a -t 192.168.40.2:80 -r 192.168.40.11:80 -i -w 1 <-- 注意端口被改了
-a -t 192.168.40.2:80 -r 192.168.40.12:12 -m -w 1
注意查看,我们添加的前两个real server其实是不对的!使用直接路由或者隧道模式的时候,real server需要和virtual server使用相同的端口。
分别在三个real server上启动服务:
$ cd /tmp
$ echo 10 >index.html
$ python -m SimpleHTTPServer 80
$ cd /tmp
$ echo 11 >index.html
$ python -m SimpleHTTPServer 80
$ cd /tmp
$ echo 12 >index.html
$ python -m SimpleHTTPServer 12
IP tunnel模式
IP tunnel模式中,virtual service的vip同时在LB和real server上设置,real server不能对vip的arp请求进行回应,防止报文绕过LB到达real server,ARP problem in VS/TUN and VS/DR。
Client发送到vip的报文先被LB接收,LB通过IPIP隧道转发送给real server,real server收到ipip包后解析出真实报文,然后直接回复给client。
假设要配置环境中各组件的IP如下:
lb: 192.168.40.2
realserver: 192.168.40.11
vip: 192.168.40.3
在lb上配置:
//在lb上设置vip
ifconfig eth0:0 192.168.40.3 netmask 255.255.255.255 broadcast 192.168.40.3 up
ip addr add 192.168.40.3 dev eth1
//开启IP转发
echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
//配置virtual service的vip
ipvsadm -A -t 192.168.40.3:80 -s rr
ipvsadm -a -t 192.168.40.3:80 -r 192.168.40.11 -i //注意是real server的IP
在realserver上配置:
//在real server上设置vip
ifconfig tunl0 192.168.40.3 netmask 255.255.255.255 broadcast 192.168.40.3 up
route add -host 192.168.40.3 dev tunl0
//tunl0网卡不回应vip的arp请求
echo 8 >/proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/tunl0/arp_ignore
//对外网卡设置为对目标地址是自己的IP的arp请求进行回应
echo 2 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/eth1/arp_ignore
//将tunl0的源地址验证改为松散模式,否网rs不会响应vip
echo 2 >/proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/tunl0/rp_filter
然后用client访问192.168.40.3,在real server对外的网卡上可以抓取到下面的ipip报文:
# tcpdump -a -i eth1 host 192.168.40.2
tcpdump: verbose output suppressed, use -v or -vv for full protocol decode
listening on eth1, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), capture size 262144 bytes
12:45:11.105289 IP 192.168.40.2 > 192.168.40.11: IP 192.168.40.1.62855 > 192.168.40.3.http: Flags ..., length 0 (ipip-proto-4)
12:45:11.105545 IP 192.168.40.2 > 192.168.40.11: IP 192.168.40.1.62855 > 192.168.40.3.http: Flags ..., length 0 (ipip-proto-4)
12:45:11.105551 IP 192.168.40.2 > 192.168.40.11: IP 192.168.40.1.62855 > 192.168.40.3.http: Flags ..., length 76: HTTP: GET / HTTP/1.1 (ipip-proto-4)
12:45:11.106538 IP 192.168.40.2 > 192.168.40.11: IP 192.168.40.1.62855 > 192.168.40.3.http: Flags ..., length 0 (ipip-proto-4)
12:45:11.106685 IP 192.168.40.2 > 192.168.40.11: IP 192.168.40.1.62855 > 192.168.40.3.http: Flags ..., length 0 (ipip-proto-4)
12:45:11.106782 IP 192.168.40.2 > 192.168.40.11: IP 192.168.40.1.62855 > 192.168.40.3.http: Flags ..., length 0 (ipip-proto-4)
12:45:11.106787 IP 192.168.40.2 > 192.168.40.11: IP 192.168.40.1.62855 > 192.168.40.3.http: Flags ..., length 0 (ipip-proto-4)
12:45:11.107139 IP 192.168.40.2 > 192.168.40.11: IP 192.168.40.1.62855 > 192.168.40.3.http: Flags ..., length 0 (ipip-proto-4)
可以看到real server的对外网卡上只收到了来自LB的ipip报文,real server的回应报文是直接返回给client的,不经过LB。
涉及到的内核参数
linux/Documentation/networking/ip-sysctl.txt
arp_filter - BOOLEAN:
default 0,The kernel can respond to arp requests with addresses
from other interfaces.
1,have the ARPs for each interface be answered
based on whether or not the kernel would route a packet from
the ARP'd IP out that interface
arp_announce - INTEGER:
Define different restriction levels for announcing the local
source IP address from IP packets in ARP requests sent on
interface:
default 0,Use any local address, configured on any interface
1,try to avoid local addresses that are not in the target's
subnet for this interface.
2,ignore the source address in the IP packet and try to select
local address that we prefer for talks with the target host.
arp_ignore - INTEGER:
default 0, reply for any local target IP address, configured
on any interface
1,reply only if the target IP address is local address
configured on the incoming interface
2,reply only if the target IP address is local address
configured on the incoming interface and both with the
sender's IP address are part from same subnet on this interface
3,do not reply for local addresses configured with scope host,
only resolutions for global and link addresses are replied
4-7 - reserved
8 - do not reply for all local addresses
arp_notify - BOOLEAN:
Define mode for notification of address and device changes.
default 0,do nothing
1,Generate gratuitous arp requests when device is brought up
or hardware address changes.
arp_accept - BOOLEAN:
Define behavior for gratuitous ARP frames who's IP is not
already present in the ARP table:
0,don't create new entries in the ARP table
1,create new entries in the ARP table
rp_filter - INTEGER:
0 - No source validation.
1 - Strict mode as defined in RFC3704 Strict Reverse Path
Each incoming packet is tested against the FIB and if the interface
is not the best reverse path the packet check will fail.
By default failed packets are discarded.
2 - Loose mode as defined in RFC3704 Loose Reverse Path
Each incoming packet's source address is also tested against the FIB
and if the source address is not reachable via any interface
the packet check will fail.
